The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Nephrology
[Changes/new developments in pediatric nephrology II.]
[In infancy, febrile urinary tract infection is common. Its symptoms are often poor. If treatment is started in time, recovery is usually quick, and the chance of kidney damage is minimal.]
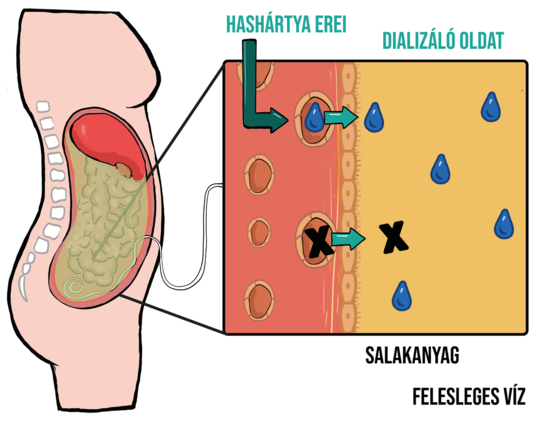
[Peritoneal dialysis in practice – a clinician’s perspective not just for nephrologists]
[As the number of patients requiring renal replacement therapy increases, so does the number of patients requiring peritoneal dialysis (PD). In fact, peritoneal dialysis is an effective and well tolerated renal replacement therapy for a wide spectrum of kidney diseases, regardless of age, even for elderly patients.]
[Epidemiological overview: frekvency of chronic kidney diseases and kidney replacement therapy]
[Based on international and domestic data, the author presents the dynamic increase in the number of chronic kidney patients and the growing burden of caring for end-stage kidney patients (renal replacement treatments, high risk of death and hospitalization) – wich are associated with a significant increase in healthcare cost. He considers the early diagnosis and adequate conservative treatment of the disease to be important.]
[Menorrhagia associated with anticoagulant treatment of young thromboembolic female patients ]
[Venous thromboembolism can occur also at young age and needs long-term anticoagulant treatment in specific cases. However, young women on anticoagulant therapy face special problems. One of the most common ones is an increasing and often heavy menstrual bleeding, which may result in anaemia. All anticoagulants can provoke menorrhagia and according to the available evidence, it is mostly associated with administration of activated factor X-inhibitors. Its management requires cooperation of gynaecologists and haematologists. Most cases are well controlled by adjusting the anticoagulant therapy, using hormonal therapy orally or via intrauterine device or administration of antifibrinolytic agents. However, some cases require surgical treatment. While caring for these patients, it is essential to explore the problem by taking accurate history and adequate laboratory tests, to modify the treatment and supplement the loss of iron alleviating this way the symptoms and improving the patient’s quality of life as well. ]
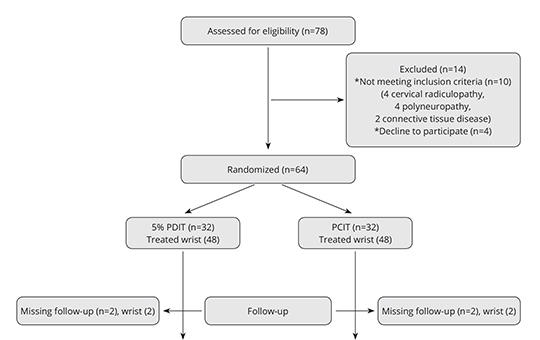
Perineural 5% dextrose versus corticosteroid injection in non-surgical carpal tunnel syndrom treatment
We aimed to investigate the difference of clinical and electrophysiological improvement between perineural corticosteroid injection therapy and perineural 5% dextrose injection therapy in carpal tunnel syndrome. Total of 92 wrists that were diagnosed as mild-to-moderate idiopathic CTS and completed their follow-up were included in our study. The severity of pain, symptom severity and functional status were assessed by visual analog scale.
[Patients with diabetes, renal failure and perimenopausal hypertension]
[The determinants of cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality is sympathetic overweight, which is the main risk factor for CVD. factors - hypertension (HT), diabetes mellitus (T2DM), renal function deterioration (CKD), dyslipidaemia and, in women, the perimenopausal status - significantly potentiates the adverse effects of diabetes, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.